A number of different levels and schemas have evolved time after time.
Here you have a table repotrting, for every different level, the global capacity and realiability.
Characteristics of most common RAID levels
| Level | Min disk number | Global Capacity |
Max number | Schema |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RAID 0 | 2 | C × N | 0 |  |
| RAID 1 | 2 | C | N - 1 | 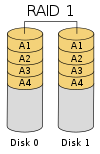 |
| RAID 3 | 3 | C × (N - 1) | 1 |  |
| RAID 4 | 3 | C × (N - 1) | 1 | 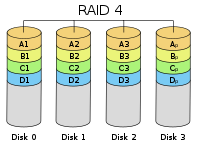 |
| RAID 5 | 3 | C × (N − 1) | 1 |  |
| RAID 6 | 4 | C × (N − 2) | 2 | 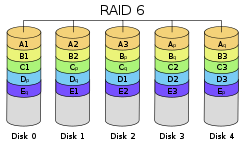 |
| C = capacity of littlest disk; N = number of disks | ||||